1. null合并运算符(??)
语法: 如果变量存在且值不为NULL,它就会返回自身的值,否则返回它的第二个操作数.
//php7以前 if判断
if(empty($_GET['param'])) {
$param = 1;
}else{
$param = $_GET['param'];
}
//php7以前 三元运算符
$param = empty($_GET['param']) ? 1 : $_GET['param'];
//PHP7 null合并运算符
$param = $_GET['param'] ?? 1;//1
2. define() 定义常量数组
//php7以前
define("CONTENT", "hello world");
echo CONTENT;//hello world
//PHP7
define('ANIMALS', [
'dog',
'cat',
'bird'
]);
echo ANIMALS[2];//bird
//PHP7 类外也可使用const来定义常量
const CONSTANT = 'Hello World';
echo CONSTANT;//Hello World
3. 组合比较符(=>)
组合比较符用于比较两个表达式.当$a小于、等于或大于$b时它分别返回-1、0或1. 比较的原则是沿用PHP的常规比较规则进行的.
/整数 echo 1 => 1; // 0 echo 1 => 2; // -1 echo 2 => 1; // 1 //浮点数 echo 1.5 => 1.5; // 0 echo 1.5 => 2.5; // -1 echo 2.5 => 1.5; // 1 //字符串 echo "a" => "a"; // 0 echo "a" => "b"; // -1 echo "b" => "a"; // 1
4. 变量类型声明
两种模式: 强制(默认)和严格模式. 可以使用下列类型参数: string,int,float,bool
//... 操作符: 表示这是一个可变参数. php5.6及以上的版本可使用: 函数定义的时候变量前使用.
function intSum(int ...$ints){
return array_sum($ints);
}
var_dump(intSum(2,'3.5'));//5
//严格模式
//模式声明:declare(strict_types=1); 默认情况值为0,值为1代表为严格校验的模式
declare(strict_types=1);
function add(int $a,int $b){
return $a+$b;
}
var_dump(add(2,'3.5')); //Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: Argument 2 passed to add() must be of the type integer
5. 返回值类型声明
增加返回类型声明的支持.类似于参数类型声明.(用法在函数定义的后面加 :类型名)
//有效的返回类型
declare(strict_types = 1);
function getInt(int $value): int {
return $value;
}
print(getInt(6));//6
//无效返回类型
declare(strict_types = 1);
function getNoInt(int $value): int {
return $value+'2.5';
}
print(getNoInt(6));//Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: Return value of getNoInt() must be of the type integer
6. 匿名类
允许new class {} 创建一个匿名的对象.
?php
//php7以前 接口实现
interface User{
public function getDiscount();
}
class VipUser implements User{
//折扣系数
private $discount = 0.6;
public function getDiscount() {
return $this->discount;
}
}
class Goods{
private $price = 200;
private $objectVipUser;
//User接口VipUser类实现
public function getUserData($User){
$this->objectVipUser = $User;
$discount = $this->objectVipUser->getDiscount();
echo "商品价格:".$this->price*$discount;
}
}
$display = new Goods();
//常规实例化接口实现对象
$display ->getUserData(new VipUser);//商品价格:120
?php
//php7 创建一个匿名的对象
interface User{
public function getDiscount();
}
class Goods{
private $price = 200;
private $objectVipUser;
public function getUserData($User){
$this->objectVipUser = $User;
$discount = $this->objectVipUser->getDiscount();
echo "商品价格:".$this->price*$discount;
}
}
$display = new Goods();
//new匿名对象实现user接口
$display ->getUserData(new class implements User{
private $discount = 0.6;
public function getDiscount() {
return $this->discount;
}
});//商品价格:120
7. Closure::call()
Closure::call() 方法被添加为一个简短的方式来临时绑定一个对象作用域到一个闭包并调用它. 与PHP5的bindTo相比.它的性能要快得多.
?php
//php7以前
class A {
private $attribute = 'hello world';
}
$getClosure = function(){
return $this->attribute;
};
$getAttribute = $getClosure->bindTo(new A, 'A');//中间层闭包
echo $getAttribute();//hello world
?php
//PHP7
class A {
private $attribute = 'hello world';
}
$getClosure = function(){
return $this->attribute;
};
echo $getClosure->call(new A);//hello world
8. unserialize()
unserialize()函数:过滤的特性,可以防止非法数据进行代码注入,提供了更安全的反序列化数据
?php
class A{
public $name = 'admin_a';
}
class B{
public $name = 'admin_b';
}
$objA = new A();
$objB = new B();
$serializedObjA = serialize($objA);
$serializedObjB = serialize($objB);
//默认行为是接收所有类; 第二个参数可以忽略
$dataA = unserialize($serializedObjA , ["allowed_classes" => true]);
var_dump($dataA);//object(A)#3 (1) { ["name"]=> string(7) "admin_a" }
//如果allowed_classes设置为false,unserialize会将所有对象转换为__PHP_Incomplete_Class对象
$dataA = unserialize($serializedObjA , ["allowed_classes" => false]);
var_dump($dataA);//object(__PHP_Incomplete_Class)#4 (2) { ["__PHP_Incomplete_Class_Name"]=> string(1) "A" ["name"]=> string(7) "admin_a" }
//转换所有对象到 __PHP_Incomplete_Class对象,除了对象"B"
$dataB = unserialize($serializedObjB , ["allowed_classes" => ["B"]]);
var_dump($dataB);//object(B)#3 (1) { ["name"]=> string(7) "admin_b" }
9. IntlChar
IntlChar:提供了一些可用于访问Unicode字符信息的实用方法的访问. 注意:必须安装Intl扩展才能使用!
var_dump(IntlChar::CODEPOINT_MAX);//int(1114111)
echo 'br>';
var_dump(IntlChar::charName('+'));//string(9) "PLUS SIGN"
echo 'br>';
var_dump(IntlChar::ispunct('?'));//bool(true)
10. CSPRNG
CSPRNG 函数提供一种简单的机制来生成密码的随机数.
random_bytes() -加密生存被保护的伪随机字符串.
random_int() -加密生存被保护的伪随机整数.
$bytes = random_bytes(8); echo(bin2hex($bytes));//随机2073a110a2e3c497 echo 'br>'; echo(random_int(1, 999));//随机786 echo 'br>'; print(random_int(-999, -1));//随机-357
11. use 语句
可以使用单个use语句从相同的命名空间导入类,函数和常量,而不是使用多个use语句.
//PHP7之前
use some\namespace\ClassA;
use some\namespace\ClassB;
use some\namespace\ClassC as C;
use function some\namespace\fn_a;
use function some\namespace\fn_b;
use function some\namespace\fn_c;
use const some\namespace\ConstA;
use const some\namespace\ConstB;
use const some\namespace\ConstC;
// PHP7之后
use some\namespace\{ClassA, ClassB, ClassC as C};
use function some\namespace\{fn_a, fn_b, fn_c};
use const some\namespace\{ConstA, ConstB, ConstC};
12. intp
新增加intp()函数,接收两个参数,返回值为第一个参数除于第二个参数的值并取整.
echo intp(8,4);//2 echo intp(10,4);//2 echo intp(5,10);//0
13. PHP7 错误处理
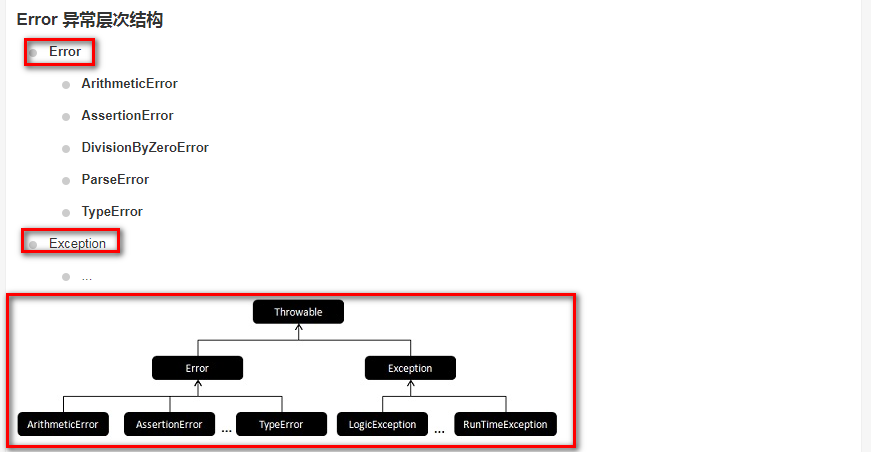
PHP7 改变了大多数错误的报告方式.不同于PHP5的传统错误报告机制,现在大多数错误被作为Error异常抛出.
这种Error异常可以像普通异常一样被try / catch块所捕获. 如果没有匹配的try / catch块,则调用异常处理函数(由 set_exception_handler() 注册)进行处理.
如果尚未注册异常处理函数,则按照传统方式处理:被报告为一个致命错误(Fatal Error).
Error类并不是从Exception类扩展出来的,所以用catch (Exception $e) { ... } 这样的代码是捕获不到Error的.你可以用 catch (Error $e) { ... } 这样的代码,
或者通过注册异常处理函数( set_exception_handler())来捕获Error.
?php
//php7以前 自定义异常处理
class getException extends Exception{
public function errorMsg(){
return '错误的信息'.$this->getMessage().'br>错误的代码'.$this->getCode();
}
}
try {
$num =10;
if($num > 1) {
throw new getException($num,404);
}
} catch (getException $e) {
echo $e->errorMsg();
}
?php
//php7 异常处理
try {
test();
}catch(Error $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();//Call to undefined function test()
}
上一篇:PHP7新功能总结