readlines的帮助信息
>>> fr=open('readme.txt')
>>> help(fr.readlines)
Help on built-in function readlines:
readlines(hint=-1, /) method of _io.TextIOWrapper instance
Return a list of lines from the stream.
hint can be specified to control the number of lines read: no more
lines will be read if the total size (in bytes/characters) of all
lines so far exceeds hint.
Google翻译
_io.TextIOWrapper 实例的 readlines(hint=-1, /) 方法
从流中返回行列表。
可以指定 hint 来控制读取的行数:如果到目前为止所有行的总大小(以字节/字符为单位)超过hint,则不会读取更多行。
readme.txt中的内容

>>> f=open('readme.txt')
>>> f.readlines()
['1\n', '22\n', '\n', '333']
为了进一步搞清楚hint,我写了一个函数来演示
readlines函数代码
def readlinesFile(filename,nbyte):
'''
探索f.readlines(i)中i的作用,典型的调用形式:
readlinesFile('readme.txt',12)
'''
for i in range(nbyte):
f=open(filename)
ss=f.readlines(i)
if i==0:#如果hint=0,先把每一个元素输出
textline=len(ss)#文件的总行数
ntotalbyte=0#文件的总字数
nwritebyte=0#已经写了的字节数
for j in range(textline):
#nwritebyte=ntotalbyte#已经写了的字节数
ntotalbyte=ntotalbyte+len(ss[j])
rowbyte=0#已经写了的新行的字节数,用来记一行已经输出的字节个数
while nwritebytentotalbyte:#当已写字节总字节数
print(f'{nwritebyte+1}:',repr(ss[j][rowbyte])) #repr是为了输出换行符
nwritebyte=nwritebyte+1
rowbyte=rowbyte+1
print(f'行数={textline},字数={ntotalbyte}')
print(f'f.readlines{i}={ss}')
f.close()
输出
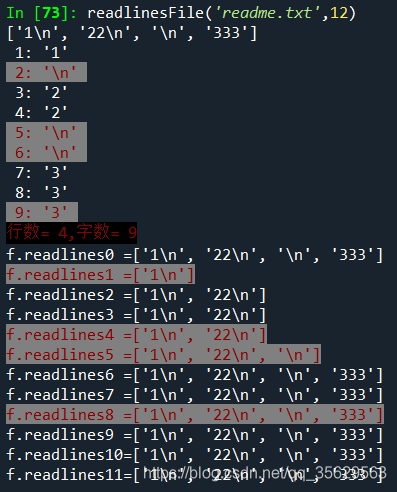
>>> readlinesFile('readme.txt',12)
1: '1'
2: '\n'
3: '2'
4: '2'
5: '\n'
6: '\n'
7: '3'
8: '3'
9: '3'
行数=4,字数=9
f.readlines0=['1\n', '22\n', '\n', '333']
f.readlines1=['1\n']
f.readlines2=['1\n', '22\n']
f.readlines3=['1\n', '22\n']
f.readlines4=['1\n', '22\n']
f.readlines5=['1\n', '22\n', '\n']
f.readlines6=['1\n', '22\n', '\n', '333']
f.readlines7=['1\n', '22\n', '\n', '333']
f.readlines8=['1\n', '22\n', '\n', '333']
f.readlines9=['1\n', '22\n', '\n', '333']
f.readlines10=['1\n', '22\n', '\n', '333']
f.readlines11=['1\n', '22\n', '\n', '333']
总结:
1.hint 是要输出显示的字节数
2.hint 默认等于-1,就是以列表的形式读出所有内容
3.hint = 0时,效果等同于-1
4.hint 所指的字节数正好是换行符的话,则实际输出是 hint+1
更花哨的readlinesFile
def readlinesFile(filename,nbyte):
'''
探索f.readlines(i)中i是指什么,典型的调用形式:
readlinesFile('readme.txt',12)
'''
specialByte=[]#存储特殊的字节数用
for i in range(nbyte):
with open(filename) as f:#使用with语句就可以不使用f.close()了
ss=f.readlines(i)
if(i==0):#如果hint=0,先把每一个元素输出
print(ss)
textline=len(ss)#文件的总行数
ntotalbyte=0#文件的总字数
nwritebyte=0#已经写了的字节数
for j in range(textline):
#nwritebyte=ntotalbyte#已经写了的字节数
ntotalbyte=ntotalbyte+len(ss[j])
rowbyte=0#已经写了的新行的字节数,用来记一行已经输出的字节个数
while nwritebytentotalbyte:#当已写字节总字节数
if(nwritebyte is ntotalbyte-1):
specialByte.append(nwritebyte)
print(f'\033[0;31;47m{nwritebyte+1:2d}:',repr(ss[j][rowbyte]),'\033[0m')#\033[0m是字体和背景颜色设置,注意可能需要其他库的支持
else:
print(f'{nwritebyte+1:2d}:',repr(ss[j][rowbyte]))
nwritebyte=nwritebyte+1
rowbyte=rowbyte+1
print(f'\033[0;31;40m行数={textline:2d},字数={ntotalbyte:2d}\033[0m')
if i in specialByte:
print(f'\033[0;31;47mf.readlines{i:2d}={ss}\033[0m') #是左对齐
else:
print(f'f.readlines{i:2d}={ss}') #是左对齐
效果
参考文章:https://www.jb51.net/article/206578.htm
到此这篇关于关于python中readlines函数的参数hint的相关知识总结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python readlines函数内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:- Python 整行读取文本方法并去掉readlines换行\n操作
- python: line=f.readlines()消除line中\n的方法
- Python File readlines() 使用方法
- 详谈python read readline readlines的区别
- Python中read()、readline()和readlines()三者间的区别和用法
- Python中read,readline和readlines的区别案例详解