主要的数据有两个:
1.小黄鸡的聊天语料:噪声很大

2.微博的标题和评论:质量相对较高

由于数据中存到大量的噪声,可以对其进行基础的处理,然后分别把input和target使用两个文件保存,即input中的第N行尾问,target的第N行为答
后续可能会把单个字作为特征(存放在input_word.txt),也可能会把词语作为特征(input.txt)
def format_xiaohuangji_corpus(word=False):
"""处理小黄鸡的语料"""
if word:
corpus_path = "./chatbot/corpus/xiaohuangji50w_nofenci.conv"
input_path = "./chatbot/corpus/input_word.txt"
output_path = "./chatbot/corpus/output_word.txt"
else:
corpus_path = "./chatbot/corpus/xiaohuangji50w_nofenci.conv"
input_path = "./chatbot/corpus/input.txt"
output_path = "./chatbot/corpus/output.txt"
f_input = open(input_path, "a")
f_output = open(output_path, "a")
pair = []
for line in tqdm(open(corpus_path), ascii=True):
if line.strip() == "E":
if not pair:
continue
else:
assert len(pair) == 2, "长度必须是2"
if len(pair[0].strip()) >= 1 and len(pair[1].strip()) >= 1:
f_input.write(pair[0] + "\n")
f_output.write(pair[1] + "\n")
pair = []
elif line.startswith("M"):
line = line[1:]
if word:
pair.append(" ".join(list(line.strip())))
else:
pair.append(" ".join(jieba_cut(line.strip())))
def format_weibo(word=False):
"""
微博数据存在一些噪声,未处理
:return:
"""
if word:
origin_input = "./chatbot/corpus/stc_weibo_train_post"
input_path = "./chatbot/corpus/input_word.txt"
origin_output = "./chatbot/corpus/stc_weibo_train_response"
output_path = "./chatbot/corpus/output_word.txt"
else:
origin_input = "./chatbot/corpus/stc_weibo_train_post"
input_path = "./chatbot/corpus/input.txt"
origin_output = "./chatbot/corpus/stc_weibo_train_response"
output_path = "./chatbot/corpus/output.txt"
f_input = open(input_path, "a")
f_output = open(output_path, "a")
with open(origin_input) as in_o, open(origin_output) as out_o:
for _in, _out in tqdm(zip(in_o, out_o), ascii=True):
_in = _in.strip()
_out = _out.strip()
if _in.endswith(")") or _in.endswith("」") or _in.endswith(")"):
_in = re.sub("(.*)|「.*?」|\(.*?\)", " ", _in)
_in = re.sub("我在.*?alink|alink|(.*?\d+x\d+.*?)|#|】|【|-+|_+|via.*?:*.*", " ", _in)
_in = re.sub("\s+", " ", _in)
if len(_in) 1 or len(_out) 1:
continue
if word:
_in = re.sub("\s+", "", _in) # 转化为一整行,不含空格
_out = re.sub("\s+", "", _out)
if len(_in) >= 1 and len(_out) >= 1:
f_input.write(" ".join(list(_in)) + "\n")
f_output.write(" ".join(list(_out)) + "\n")
else:
if len(_in) >= 1 and len(_out) >= 1:
f_input.write(_in.strip() + "\n")
f_output.write(_out.strip() + "\n")
f_input.close()
f_output.close()

和之前的操作相同,需要把文本能转化为数字,同时还需实现方法把数字转化为文本
示例代码:
import config
import pickle
class Word2Sequence():
UNK_TAG = "UNK"
PAD_TAG = "PAD"
SOS_TAG = "SOS"
EOS_TAG = "EOS"
UNK = 0
PAD = 1
SOS = 2
EOS = 3
def __init__(self):
self.dict = {
self.UNK_TAG: self.UNK,
self.PAD_TAG: self.PAD,
self.SOS_TAG: self.SOS,
self.EOS_TAG: self.EOS
}
self.count = {}
self.fited = False
def to_index(self, word):
"""word -> index"""
assert self.fited == True, "必须先进行fit操作"
return self.dict.get(word, self.UNK)
def to_word(self, index):
"""index -> word"""
assert self.fited, "必须先进行fit操作"
if index in self.inversed_dict:
return self.inversed_dict[index]
return self.UNK_TAG
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dict)
def fit(self, sentence):
"""
:param sentence:[word1,word2,word3]
:param min_count: 最小出现的次数
:param max_count: 最大出现的次数
:param max_feature: 总词语的最大数量
:return:
"""
for a in sentence:
if a not in self.count:
self.count[a] = 0
self.count[a] += 1
self.fited = True
def build_vocab(self, min_count=1, max_count=None, max_feature=None):
# 比最小的数量大和比最大的数量小的需要
if min_count is not None:
self.count = {k: v for k, v in self.count.items() if v >= min_count}
if max_count is not None:
self.count = {k: v for k, v in self.count.items() if v = max_count}
# 限制最大的数量
if isinstance(max_feature, int):
count = sorted(list(self.count.items()), key=lambda x: x[1])
if max_feature is not None and len(count) > max_feature:
count = count[-int(max_feature):]
for w, _ in count:
self.dict[w] = len(self.dict)
else:
for w in sorted(self.count.keys()):
self.dict[w] = len(self.dict)
# 准备一个index->word的字典
self.inversed_dict = dict(zip(self.dict.values(), self.dict.keys()))
def transform(self, sentence, max_len=None, add_eos=False):
"""
实现吧句子转化为数组(向量)
:param sentence:
:param max_len:
:return:
"""
assert self.fited, "必须先进行fit操作"
r = [self.to_index(i) for i in sentence]
if max_len is not None:
if max_len > len(sentence):
if add_eos:
r += [self.EOS] + [self.PAD for _ in range(max_len - len(sentence) - 1)]
else:
r += [self.PAD for _ in range(max_len - len(sentence))]
else:
if add_eos:
r = r[:max_len - 1]
r += [self.EOS]
else:
r = r[:max_len]
else:
if add_eos:
r += [self.EOS]
# print(len(r),r)
return r
def inverse_transform(self, indices):
"""
实现从数组 转化为 向量
:param indices: [1,2,3....]
:return:[word1,word2.....]
"""
sentence = []
for i in indices:
word = self.to_word(i)
sentence.append(word)
return sentence
# 之后导入该word_sequence使用
word_sequence = pickle.load(open("./pkl/ws.pkl", "rb")) if not config.use_word else pickle.load(
open("./pkl/ws_word.pkl", "rb"))
if __name__ == '__main__':
from word_sequence import Word2Sequence
from tqdm import tqdm
import pickle
word_sequence = Word2Sequence()
# 词语级别
input_path = "../corpus/input.txt"
target_path = "../corpus/output.txt"
for line in tqdm(open(input_path).readlines()):
word_sequence.fit(line.strip().split())
for line in tqdm(open(target_path).readlines()):
word_sequence.fit(line.strip().split())
# 使用max_feature=5000个数据
word_sequence.build_vocab(min_count=5, max_count=None, max_feature=5000)
print(len(word_sequence))
pickle.dump(word_sequence, open("./pkl/ws.pkl", "wb"))
word_sequence.py:
class WordSequence(object):
PAD_TAG = 'PAD' # 填充标记
UNK_TAG = 'UNK' # 未知词标记
SOS_TAG = 'SOS' # start of sequence
EOS_TAG = 'EOS' # end of sequence
PAD = 0
UNK = 1
SOS = 2
EOS = 3
def __init__(self):
self.dict = {
self.PAD_TAG: self.PAD,
self.UNK_TAG: self.UNK,
self.SOS_TAG: self.SOS,
self.EOS_TAG: self.EOS
}
self.count = {} # 保存词频词典
self.fited = False
def to_index(self, word):
"""
word --> index
:param word:
:return:
"""
assert self.fited == True, "必须先进行fit操作"
return self.dict.get(word, self.UNK)
def to_word(self, index):
"""
index -- > word
:param index:
:return:
"""
assert self.fited, '必须先进行fit操作'
if index in self.inverse_dict:
return self.inverse_dict[index]
return self.UNK_TAG
def fit(self, sentence):
"""
传入句子,统计词频
:param sentence:
:return:
"""
for word in sentence:
# 对word出现的频率进行统计,当word不在sentence时,返回值是0,当word在sentence中时,返回+1,以此进行累计计数
# self.count[word] = self.dict.get(word, 0) + 1
if word not in self.count:
self.count[word] = 0
self.count[word] += 1
self.fited = True
def build_vocab(self, min_count=2, max_count=None, max_features=None):
"""
构造词典
:param min_count:最小词频
:param max_count: 最大词频
:param max_features: 词典中词的数量
:return:
"""
# self.count.pop(key),和del self.count[key] 无法在遍历self.count的同时进行删除key.因此浅拷贝temp后对temp遍历并删除self.count
temp = self.count.copy()
for key in temp:
cur_count = self.count.get(key, 0) # 当前词频
if min_count is not None:
if cur_count min_count:
del self.count[key]
if max_count is not None:
if cur_count > max_count:
del self.count[key]
if max_features is not None:
self.count = dict(sorted(list(self.count.items()), key=lambda x: x[1], reversed=True)[:max_features])
for key in self.count:
self.dict[key] = len(self.dict)
# 准备一个index-->word的字典
self.inverse_dict = dict(zip(self.dict.values(), self.dict.keys()))
def transforms(self, sentence, max_len=10, add_eos=False):
"""
把sentence转化为序列
:param sentence: 传入的句子
:param max_len: 句子的最大长度
:param add_eos: 是否添加结束符
add_eos : True时,输出句子长度为max_len + 1
add_eos : False时,输出句子长度为max_len
:return:
"""
assert self.fited, '必须先进行fit操作!'
if len(sentence) > max_len:
sentence = sentence[:max_len]
# 提前计算句子长度,实现ass_eos后,句子长度统一
sentence_len = len(sentence)
# sentence[1,3,4,5,UNK,EOS,PAD,....]
if add_eos:
sentence += [self.EOS_TAG]
if sentence_len max_len:
# 句子长度不够,用PAD来填充
sentence += (max_len - sentence_len) * [self.PAD_TAG]
# 对于新出现的词采用特殊标记
result = [self.dict.get(i, self.UNK) for i in sentence]
return result
def invert_transform(self, indices):
"""
序列转化为sentence
:param indices:
:return:
"""
# return [self.inverse_dict.get(i, self.UNK_TAG) for i in indices]
result = []
for i in indices:
if self.inverse_dict[i] == self.EOS_TAG:
break
result.append(self.inverse_dict.get(i, self.UNK_TAG))
return result
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dict)
if __name__ == '__main__':
num_sequence = WordSequence()
print(num_sequence.dict)
str1 = ['中国', '您好', '我爱你', '中国', '我爱你', '北京']
num_sequence.fit(str1)
num_sequence.build_vocab()
print(num_sequence.transforms(str1))
print(num_sequence.dict)
print(num_sequence.inverse_dict)
print(num_sequence.invert_transform([5, 4])) # 这儿要传列表
运行结果:

创建dataset.py 文件,准备数据集
import config
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from word_sequence import WordSequence
class ChatDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self):
self.input_path = config.chatbot_input_path
self.target_path = config.chatbot_target_path
self.input_lines = open(self.input_path, encoding='utf-8').readlines()
self.target_lines = open(self.target_path, encoding='utf-8').readlines()
assert len(self.input_lines) == len(self.target_lines), 'input和target长度不一致'
def __getitem__(self, item):
input = self.input_lines[item].strip().split()
target = self.target_lines[item].strip().split()
if len(input) == 0 or len(target) == 0:
input = self.input_lines[item + 1].strip().split()
target = self.target_lines[item + 1].strip().split()
# 此处句子的长度如果大于max_len,那么应该返回max_len
input_length = min(len(input), config.max_len)
target_length = min(len(target), config.max_len)
return input, target, input_length, target_length
def __len__(self):
return len(self.input_lines)
def collate_fn(batch):
# 1.排序
batch = sorted(batch, key=lambda x: x[2], reversed=True)
input, target, input_length, target_length = zip(*batch)
# 2.进行padding的操作
input = torch.LongTensor([WordSequence.transform(i, max_len=config.max_len) for i in input])
target = torch.LongTensor([WordSequence.transforms(i, max_len=config.max_len, add_eos=True) for i in target])
input_length = torch.LongTensor(input_length)
target_length = torch.LongTensor(target_length)
return input, target, input_length, target_length
data_loader = DataLoader(dataset=ChatDataset(), batch_size=config.batch_size, shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn,
drop_last=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(len(data_loader))
for idx, (input, target, input_length, target_length) in enumerate(data_loader):
print(idx)
print(input)
print(target)
print(input_length)
print(target_length)
encode.py:
import torch.nn as nn
import config
from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pad_packed_sequence, pack_padded_sequence
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
# torch.nn.Embedding(num_embeddings词典大小即不重复词数,embedding_dim单个词用多长向量表示)
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(
num_embeddings=len(config.word_sequence.dict),
embedding_dim=config.embedding_dim,
padding_idx=config.word_sequence.PAD
)
self.gru = nn.GRU(
input_size=config.embedding_dim,
num_layers=config.num_layer,
hidden_size=config.hidden_size,
bidirectional=False,
batch_first=True
)
def forward(self, input, input_length):
"""
:param input: [batch_size, max_len]
:return:
"""
embedded = self.embedding(input) # embedded [batch_size, max_len, embedding_dim]
# 加速循环过程
embedded = pack_padded_sequence(embedded, input_length, batch_first=True) # 打包
out, hidden = self.gru(embedded)
out, out_length = pad_packed_sequence(out, batch_first=True, padding_value=config.num_sequence.PAD) # 解包
# hidden即h_n [num_layer*[1/2],batchsize, hidden_size]
# out : [batch_size, seq_len/max_len, hidden_size]
return out, hidden, out_length
if __name__ == '__main__':
from dataset import data_loader
encoder = Encoder()
print(encoder)
for input, target, input_length, target_length in data_loader:
out, hidden, out_length = encoder(input, input_length)
print(input.size())
print(out.size())
print(hidden.size())
print(out_length)
break
decode.py:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import config
import torch.nn.functional as F
from word_sequence import WordSequence
class Decode(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.max_seq_len = config.max_len
self.vocab_size = len(WordSequence)
self.embedding_dim = config.embedding_dim
self.dropout = config.dropout
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=self.vocab_size, embedding_dim=self.embedding_dim,
padding_idx=WordSequence.PAD)
self.gru = nn.GRU(input_size=self.embedding_dim, hidden_size=config.hidden_size, num_layers=1, batch_first=True,
dropout=self.dropout)
self.log_softmax = nn.LogSoftmax()
self.fc = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, self.vocab_size)
def forward(self, encoder_hidden, target, target_length):
# encoder_hidden [batch_size,hidden_size]
# target [batch_size,seq-len]
decoder_input = torch.LongTensor([[WordSequence.SOS]] * config.batch_size).to(config.device)
decoder_outputs = torch.zeros(config.batch_size, config.max_len, self.vocab_size).to(
config.device) # [batch_size,seq_len,14]
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden # [batch_size,hidden_size]
for t in range(config.max_len):
decoder_output_t, decoder_hidden = self.forward_step(decoder_input, decoder_hidden)
decoder_outputs[:, t, :] = decoder_output_t
value, index = torch.topk(decoder_output_t, 1) # index [batch_size,1]
decoder_input = index
return decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden
def forward_step(self, decoder_input, decoder_hidden):
"""
:param decoder_input:[batch_size,1]
:param decoder_hidden:[1,batch_size,hidden_size]
:return:[batch_size,vocab_size],decoder_hidden:[1,batch_size,didden_size]
"""
embeded = self.embedding(decoder_input) # embeded: [batch_size,1 , embedding_dim]
out, decoder_hidden = self.gru(embeded, decoder_hidden) # out [1, batch_size, hidden_size]
out = out.squeeze(0)
out = F.log_softmax(self.fc(out), dim=1) # [batch_Size, vocab_size]
out = out.squeeze(0)
# print("out size:",out.size(),decoder_hidden.size())
return out, decoder_hidden
关于 decoder_outputs[:,t,:] = decoder_output_t的演示
decoder_outputs 形状 [batch_size, seq_len, vocab_size] decoder_output_t 形状[batch_size, vocab_size]
示例代码:
import torch a = torch.zeros((2, 3, 5)) print(a.size()) print(a) b = torch.randn((2, 5)) print(b.size()) print(b) a[:, 0, :] = b print(a.size()) print(a)
运行结果:

关于torch.topk, torch.max(),torch.argmax()
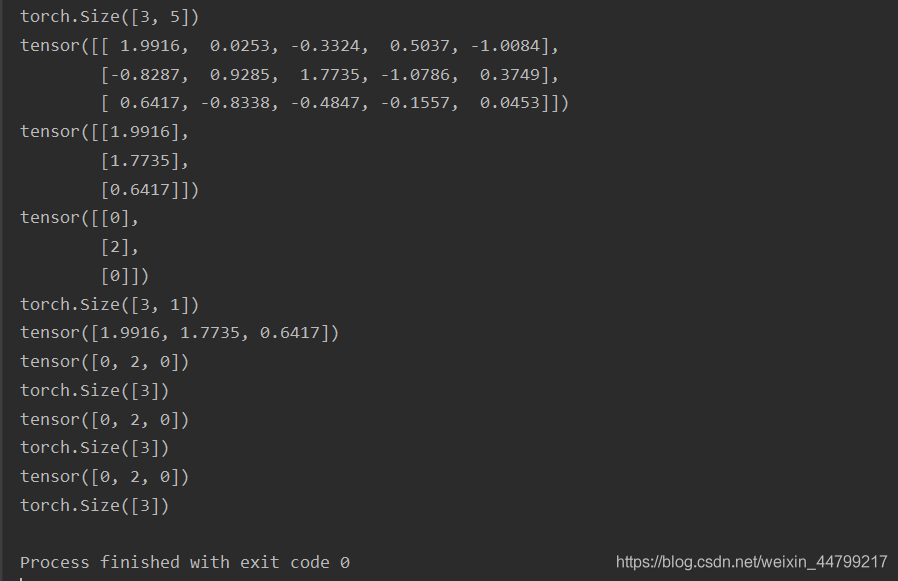
value, index = torch.topk(decoder_output_t , k = 1) decoder_output_t [batch_size, vocab_size]
示例代码:
import torch a = torch.randn((3, 5)) print(a.size()) print(a) values, index = torch.topk(a, k=1) print(values) print(index) print(index.size()) values, index = torch.max(a, dim=-1) print(values) print(index) print(index.size()) index = torch.argmax(a, dim=-1) print(index) print(index.size()) index = a.argmax(dim=-1) print(index) print(index.size())
运行结果:
若使用teacher forcing ,将采用下次真实值作为下个time step的输入
# 注意unsqueeze 相当于浅拷贝,不会对原张量进行修改 decoder_input = target[:,t].unsqueeze(-1) target 形状 [batch_size, seq_len] decoder_input 要求形状[batch_size, 1]
示例代码:
import torch a = torch.randn((3, 5)) print(a.size()) print(a) b = a[:, 3] print(b.size()) print(b) c = b.unsqueeze(-1) print(c.size()) print(c)
运行结果:

seq2seq.py:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder):
super(Seq2Seq, self).__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self, input, target, input_length, target_length):
encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden = self.encoder(input, input_length)
decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden = self.decoder(encoder_hidden, target, target_length)
return decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden
def evaluation(self, inputs, input_length):
encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden = self.encoder(inputs, input_length)
decoded_sentence = self.decoder.evaluation(encoder_hidden)
return decoded_sentence
为了加速训练,可以考虑在gpu上运行,那么在我们自顶一个所以的tensor和model都需要转化为CUDA支持的类型。
当前的数据量为500多万条,在GTX1070(8G显存)上训练,大概需要90分一个epoch,耐心的等待吧
train.py:
import torch
import config
from torch import optim
import torch.nn as nn
from encode import Encoder
from decode import Decoder
from seq2seq import Seq2Seq
from dataset import data_loader as train_dataloader
from word_sequence import WordSequence
encoder = Encoder()
decoder = Decoder()
model = Seq2Seq(encoder, decoder)
# device在config文件中实现
model.to(config.device)
print(model)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("model/seq2seq_model.pkl"))
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters())
optimizer.load_state_dict(torch.load("model/seq2seq_optimizer.pkl"))
criterion = nn.NLLLoss(ignore_index=WordSequence.PAD, reduction="mean")
def get_loss(decoder_outputs, target):
target = target.view(-1) # [batch_size*max_len]
decoder_outputs = decoder_outputs.view(config.batch_size * config.max_len, -1)
return criterion(decoder_outputs, target)
def train(epoch):
for idx, (input, target, input_length, target_len) in enumerate(train_dataloader):
input = input.to(config.device)
target = target.to(config.device)
input_length = input_length.to(config.device)
target_len = target_len.to(config.device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
##[seq_len,batch_size,vocab_size] [batch_size,seq_len]
decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden = model(input, target, input_length, target_len)
loss = get_loss(decoder_outputs, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, idx * len(input), len(train_dataloader.dataset),
100. * idx / len(train_dataloader), loss.item()))
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "model/seq2seq_model.pkl")
torch.save(optimizer.state_dict(), 'model/seq2seq_optimizer.pkl')
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(10):
train(i)
训练10个epoch之后的效果如下,可以看出损失依然很高:
Train Epoch: 9 [2444544/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.923604 Train Epoch: 9 [2444800/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.364594 Train Epoch: 9 [2445056/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.613254 Train Epoch: 9 [2445312/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.143538 Train Epoch: 9 [2445568/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.412729 Train Epoch: 9 [2445824/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.516526 Train Epoch: 9 [2446080/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.124945 Train Epoch: 9 [2446336/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.777015 Train Epoch: 9 [2446592/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.358538 Train Epoch: 9 [2446848/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.513412 Train Epoch: 9 [2447104/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.202757 Train Epoch: 9 [2447360/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.589584
decoder 中添加评估方法
def evaluate(self, encoder_hidden): """ 评估, 和fowward逻辑类似 :param encoder_hidden: encoder最后time step的隐藏状态 [1, batch_size, hidden_size] :return: """ batch_size = encoder_hidden.size(1) # 初始化一个[batch_size, 1]的SOS张量,作为第一个time step的输出 decoder_input = torch.LongTensor([[config.target_ws.SOS]] * batch_size).to(config.device) # encoder_hidden 作为decoder第一个时间步的hidden [1, batch_size, hidden_size] decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden # 初始化[batch_size, seq_len, vocab_size]的outputs 拼接每个time step结果 decoder_outputs = torch.zeros((batch_size, config.chatbot_target_max_len, self.vocab_size)).to(config.device) # 初始化一个空列表,存储每次的预测序列 predict_result = [] # 对每个时间步进行更新 for t in range(config.chatbot_target_max_len): decoder_output_t, decoder_hidden = self.forward_step(decoder_input, decoder_hidden) # 拼接每个time step,decoder_output_t [batch_size, vocab_size] decoder_outputs[:, t, :] = decoder_output_t # 由于是评估,需要每次都获取预测值 index = torch.argmax(decoder_output_t, dim = -1) # 更新下一时间步的输入 decoder_input = index.unsqueeze(1) # 存储每个时间步的预测序列 predict_result.append(index.cpu().detach().numpy()) # [[batch], [batch]...] ->[seq_len, vocab_size] # 结果转换为ndarry,每行是一个预测结果即单个字对应的索引, 所有行为seq_len长度 predict_result = np.array(predict_result).transpose() # (batch_size, seq_len)的array return decoder_outputs, predict_result
eval.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from dataset import get_dataloader
import config
import numpy as np
from Seq2Seq import Seq2SeqModel
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
model = Seq2SeqModel().to(config.device)
if os.path.exists('./model/chatbot_model.pkl'):
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./model/chatbot_model.pkl'))
def eval():
model.eval()
loss_list = []
test_data_loader = get_dataloader(train = False)
with torch.no_grad():
bar = tqdm(test_data_loader, desc = 'testing', total = len(test_data_loader))
for idx, (input, target, input_length, target_length) in enumerate(bar):
input = input.to(config.device)
target = target.to(config.device)
input_length = input_length.to(config.device)
target_length = target_length.to(config.device)
# 获取模型的预测结果
decoder_outputs, predict_result = model.evaluation(input, input_length)
# 计算损失
loss = F.nll_loss(decoder_outputs.view(-1, len(config.target_ws)), target.view(-1), ignore_index = config.target_ws.PAD)
loss_list.append(loss.item())
bar.set_description('idx{}:/{}, loss:{}'.format(idx, len(test_data_loader), np.mean(loss_list)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
eval()
interface.py:
from cut_sentence import cut
import torch
import config
from Seq2Seq import Seq2SeqModel
import os
# 模拟聊天场景,对用户输入进来的话进行回答
def interface():
# 加载训练集好的模型
model = Seq2SeqModel().to(config.device)
assert os.path.exists('./model/chatbot_model.pkl') , '请先对模型进行训练!'
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./model/chatbot_model.pkl'))
model.eval()
while True:
# 输入进来的原始字符串,进行分词处理
input_string = input('me>>:')
if input_string == 'q':
print('下次再聊')
break
input_cuted = cut(input_string, by_word = True)
# 进行序列转换和tensor封装
input_tensor = torch.LongTensor([config.input_ws.transfrom(input_cuted, max_len = config.chatbot_input_max_len)]).to(config.device)
input_length_tensor = torch.LongTensor([len(input_cuted)]).to(config.device)
# 获取预测结果
outputs, predict = model.evaluation(input_tensor, input_length_tensor)
# 进行序列转换文本
result = config.target_ws.inverse_transform(predict[0])
print('chatbot>>:', result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
interface()
config.py:
import torch
from word_sequence import WordSequence
chatbot_input_path = './corpus/input.txt'
chatbot_target_path = './corpus/target.txt'
word_sequence = WordSequence()
max_len = 9
batch_size = 128
embedding_dim = 100
num_layer = 1
hidden_size = 64
dropout = 0.1
model_save_path = './model.pkl'
optimizer_save_path = './optimizer.pkl'
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
cut.py:
"""
分词
"""
import jieba
import config1
import string
import jieba.posseg as psg # 返回词性
from lib.stopwords import stopwords
# 加载词典
jieba.load_userdict(config1.user_dict_path)
# 准备英文字符
letters = string.ascii_lowercase + '+'
def cut_sentence_by_word(sentence):
"""实现中英文分词"""
temp = ''
result = []
for word in sentence:
if word.lower() in letters:
# 如果是英文字符,则进行拼接空字符串
temp += word
else:
# 遇到汉字后,把英文先添加到结果中
if temp != '':
result.append(temp.lower())
temp = ''
result.append(word.strip())
if temp != '':
# 若英文出现在最后
result.append(temp.lower())
return result
def cut(sentence, by_word=False, use_stopwords=True, with_sg=False):
"""
:param sentence: 句子
:param by_word: T根据单个字分词或者F句子
:param use_stopwords: 是否使用停用词,默认False
:param with_sg: 是否返回词性
:return:
"""
if by_word:
result = cut_sentence_by_word(sentence)
else:
result = psg.lcut(sentence)
# psg 源码返回i.word,i.flag 即词,定义的词性
result = [(i.word, i.flag) for i in result]
# 是否返回词性
if not with_sg:
result = [i[0] for i in result]
# 是否使用停用词
if use_stopwords:
result = [i for i in result if i not in stopwords]
return result

到此这篇关于python通过Seq2Seq实现闲聊机器人的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Seq2Seq实现闲聊机器人内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
下一篇:django写单元测试的方法