若 w 为 m*1 的矩阵,x 为 m*n 的矩阵,那么通过点乘结果就会得到一个 m*n 的矩阵。
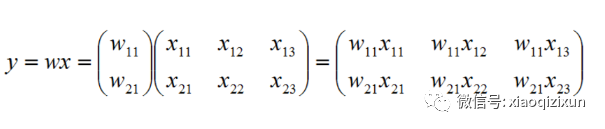
若 w 为 m*n 的矩阵,x 为 m*n 的矩阵,那么通过点乘结果就会得到一个 m*n 的矩阵。
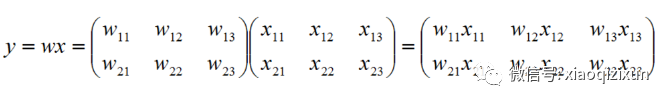
w的列数只能为 1 或 与x的列数相等(即n),w的行数与x的行数相等 才能进行乘法运算。
若 w 为 m*p 的矩阵,x 为 p*n 的矩阵,那么通过矩阵相乘结果就会得到一个 m*n 的矩阵。
只有 w 的列数 == x的行数 时,才能进行乘法运算
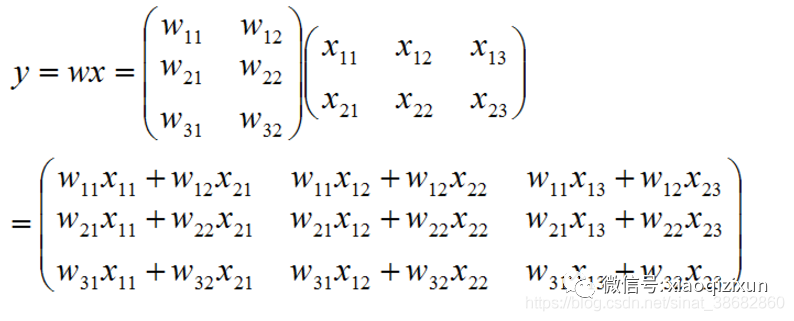
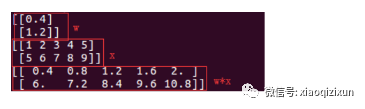
1)点乘
import numpy as np w = np.array([[0.4], [1.2]]) x = np.array([range(1,6), range(5,10)]) print w print x print w*x
运行结果如下图:
2)矩阵乘
import numpy as np w = np.array([[0.4, 1.2]]) x = np.array([range(1,6), range(5,10)]) print w print x print np.dot(w,x)
运行结果如下:

1)点乘
import tensorflow as tf w = tf.Variable([[0.4], [1.2]], dtype=tf.float32) # w.shape: [2, 1] x = tf.Variable([range(1,6), range(5,10)], dtype=tf.float32) # x.shape: [2, 5] y = w * x # 等同于 y = tf.multiply(w, x) y.shape: [2, 5] sess = tf.Session() init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) print sess.run(w) print sess.run(x) print sess.run(y)
运行结果如下:
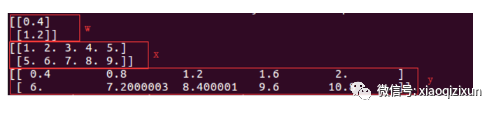
2)矩阵乘
# coding:utf-8 import tensorflow as tf w = tf.Variable([[0.4, 1.2]], dtype=tf.float32) # w.shape: [1, 2] x = tf.Variable([range(1,6), range(5,10)], dtype=tf.float32) # x.shape: [2, 5] y = tf.matmul(w, x) # y.shape: [1, 5] sess = tf.Session() init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) print sess.run(w) print sess.run(x) print sess.run(y)
运行结果如下:

到此这篇关于numpy和tensorflow中的各种乘法(点乘和矩阵乘)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关numpy和tensorflow 乘法内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!